The Cervicitis
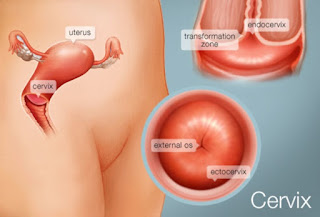
The cervix
Definition
The cervix is placed at the closure of the uterus, arriving at into the vagina. The point when the exterior tissues of the cervix get inflamed, more often than not through infection, this is called cervicitis. About 50% of all ladies will experience one session or a greater amount of cervicitis in their lifetimes. Cervicitis has several causes.
Cervicitis is an irritation of the cervix the easier part of the uterus expanding about an inch into the vaginal waterway. Most ordinarily, cervicitis is the infection, despite the fact that it can additionally be initiated by harm or irritation (a response to the chemicals in douches and contraceptives, for instance, or a disregarded tampon).
The foremost symptom of cervicitis is prone to be a vaginal discharge that comes to be more declared quickly emulating your menstrual period. Different signs include bleeding, itching, or irritation of the external genitals; pain throughout intercourse; a burning sensation throughout urination; and lower back pain. In its mildest form, you may not perceive any side effects whatsoever, yet a more intense instance of cervicitis can make a bountiful, practically discharge like, and discharge with an upsetting smell, joined by compelling vaginal irritation or stomach pain. Provided that the spoiling gets into your framework, you might additionally have fever and nausea.
Types
Cervicitis is classified according to the following types:
Acute Cervicitis
Manifestations of the acute form of the disease are expressed significantly. The patient is concerned with purulent or abundant mucosal leucorrhoea, vaginal itching and burning, which are intensified by urination. Also may be painful in cervicitis. Usually, it is a dull or aching pain in the lower abdomen, a painful intercourse. Other symptoms of the disease are due to concomitant pathology. If the inflammatory process of the cervix has arisen against the background of cystitis, worries about frequent and painful urination. With adnexitis and inflammatory process in the cervix, there is an increase in temperature from subfebrile (above 37) to febrile digits (38 and above). With the combination of pseudo-erosion and cervicitis, spotting after coition may appear. A distinctive feature of the disease is the aggravation of all clinical symptoms after menstruation.
Chronic Cervicitis
The disease, which was not adequately treated on time in an acute stage, is chronic. Symptoms of chronic cervicitis are less or less pronounced. The discharge acquires a turbid-mucous character, the flat epithelium of the vaginal part of the cervix is replaced by a cylindrical cervical channel, and pseudo-erosion of the cervix is formed. Inflammatory phenomena (redness and swelling) are poorly expressed. When the inflammation spreads to the surrounding tissues and into the interior, the cervix becomes denser, it is possible again to replace the cylindrical epithelium with the ectopia, which is accompanied by the formation of the set cysts and infiltrates.
Risk factors
You may be at higher risk for cervicitis if you:
- Had recent sexual intercourse without a condom
- Recently had multiple sexual partners
- Have had cervicitis before
Studies show that cervicitis will recur in 8% to 25% of women who get it.
Causes
- There are quite a few reasons for the emergence of cervicitis. The most common are a variety of infections of the genitals, which include both venereal diseases (gonorrhea, chlamydia, etc.), and genital herpes, candidiasis or human papillomavirus.
- The next cause of cervicitis is trauma cervix as a result of frequent sexual acts or the use of tampons during menstruation. Because of minor damage, the cervix becomes exposed to infectious processes.
- Often cervicitis is diagnosed in women who started sexually early or often change partners. Thus, these factors can also be called the causes of the appearance of the disease.
- The last cause of cervicitis is mechanical damages of the cervix, which may result from an abortion, a diagnostic curettage, or the installation of a contraceptive spiral.
Symptoms
Some cases of cervicitis in women can be symptomless. However, in most cases, symptoms are present, and they include:
- Persistence of gray or white vaginal discharge that may or may not smell
- Vaginal bleeding under certain conditions e.g. in between periods or after sex
- Pain during intercourse
- Backache
- Difficulty or pain during urination
- In rare cases, fever or pain in the abdomen
Complications
Untreated cervicitis can give rise to a host of other problems, particularly if the underlying cause is an infection. Some potential complications are listed below:
- Having cervicitis is associated with a higher risk of contracting HIV infection.
- If the patient is already HIV positive, having cervicitis can increase the probability of transmitting the virus to their partners.
- This is the inflammation of the endometrium or inner lining of the uterus.
- Inflammation of the fallopian tubes. This is known as salpingitis.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID), a severe condition that could leave the reproductive system permanently damaged.
- Infertility.
- Neonatal infections and other problems due to exposure of the fetus to infection while passing through the birth canal.
- Cervicitis may also be implicated in giving rise to cervical cancer.
Diagnosis and test
There are multiple ways cervicitis can be diagnosed.
Pelvic Exam
For this test, your doctor will insert a gloved finger into your vagina while also applying pressure to the abdomen. This way, he or she can detect abnormalities of the pelvic organs, which include the cervix.
Pap Test
For this test, also called a Pap smear, your doctor will take a swab of cells from your vagina and cervix. These cells will then be tested for abnormalities.
Cervical Biopsy
This test is often performed only if your Pap smear detected abnormalities. For this test, also called a colposcopy, your doctor will insert a speculum into your vagina. He or she will then take a cotton swab and gently clean the vagina and cervix of mucus residue. Then, the doctor will direct a light and colposcope (a type of microscope) at your vagina to examine the area. He or she will then take tissue samples from any areas that look abnormal.
The culture of Cervical Discharge for Microscopic Examination
Your doctor may also decide to take a sample of the discharge from your cervix. He or she will then place the sample under a microscope. This test can determine if you have a yeast infection (candidiasis), bacterial vaginosis, or trichomoniasis, among other conditions.
Tests for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) may also be performed. If a specific infection is contributing to your cervicitis, the infection will be treated. This should heal the cervical inflammation.
Treatment and medications
Depending on the cause of inflammation, treatment of chronic cervicitis consists of:
Symptomatic treatment of the symptoms of the chronic cervicitis if it is caused by non-infectious agents is done where the patient is prescribed medicines to reduce inflammation.
Antibiotics are prescribed if the bacterial infection is the cause of Chronic Cervicitis.
Antiviral medications are prescribed if the viral infection is the cause of Chronic Cervicitis.
Procedures such as cryotherapy and laser therapy can also be done to treat Chronic Cervicitis.
Avoiding sexual intercourse is important until the completion of treatment and until the chronic cervicitis is completely resolved. It is also important to treat the patient’s partner if the cause of chronic cervicitis is a sexually transmitted infection.
Prevention
Things you can do to reduce your risk of developing cervicitis include:
- Avoid irritants such as douches and deodorant tampons.
- Make sure that any foreign objects you insert into your vagina (such as tampons) are properly placed. Be sure to follow instructions on how long to leave it inside, how often to change it, or how often to clean it.
- Make sure your partner is free of any STI. You and your partner should not have sex with any other people.
- Use a condom every time you have sex to lower your risk of getting an STI. Condoms are available for both men and women but are most commonly worn by the man. A condom must be used properly every time.


Comments
Post a Comment