Myelodysplastic syndrome
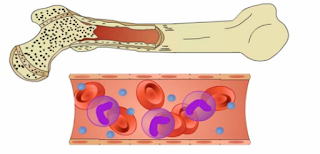
Myelodysplastic syndrome Definition MDS is a group of diseases that affect the blood and bone marrow. Bone marrow is the soft, spongy tissue inside bones. In MDS, the blood-forming cells (stem cells) in the marrow slow down, or even stop, making the 3 types of blood cells: Red blood cells – carry oxygen throughout the body White blood cells – help fight infections Platelets – help the blood clot and stop bleeding In MDS dysfunctional blood cells fail to develop normally and enter the bloodstream. As a result, individuals with MDS have abnormally low blood cell levels (low blood counts). General symptoms associated with MDS include fatigue, dizziness, weakness, bruising and bleeding, frequent infections, and headaches. In some affected individuals, MDS may progress to life-threatening failure of the bone marrow or develop into acute leukemia. The exact cause of MDS is unknown. There are no clear risk factors but genetics and the environment may play ...